A gear ratio calculator is a powerful tool used to determine the relationship between two gears in a mechanical system.
The gear reduction calculator can perform several types of conversions, such as:
- Teeth count to ratio: If you know the number of teeth on two meshing gears, the calculator can determine their ratio.
- Diameter to ratio: Using the diameters of two gears, it can calculate their ratio.
- Ratio to RPM: Given a gear ratio and the RPM of one gear, it can find the RPM of the other gear.
For example, if a driving gear has 20 teeth and a driven gear has 60 teeth, the gear ratio calculator would determine a ratio of 1:3, meaning the driven gear rotates once for every three rotations of the driving gear.
Gear Ratio Calculator
| Method | Driving Gear | Driven Gear | Calculation | Gear Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Teeth Count | 20 teeth | 60 teeth | 60 / 20 | 3:1 |
| Gear Diameter | 3 inches | 9 inches | 9 / 3 | 3:1 |
| Pitch Diameter | 2.5 inches | 7.5 inches | 7.5 / 2.5 | 3:1 |
| RPM | 3000 RPM | 1000 RPM | 3000 / 1000 | 3:1 |
Conversion equation: Gear Ratio = Driven Gear Characteristic / Driving Gear Characteristic
Related Tools
Gear Ratio Formula
- Using Teeth Count:
Gear Ratio = Number of Teeth on Driven Gear / Number of Teeth on Driving Gear - Using Gear Diameters:
Gear Ratio = Diameter of Driven Gear / Diameter of Driving Gear - Using Pitch Diameters:
Gear Ratio = Pitch Diameter of Driven Gear / Pitch Diameter of Driving Gear
Example: If a driving gear has 25 teeth and a driven gear has 75 teeth, the gear ratio would be:
Gear Ratio = 75 / 25 = 3
This means the driven gear turns once for every three rotations of the driving gear.
What is Gear Ratio?
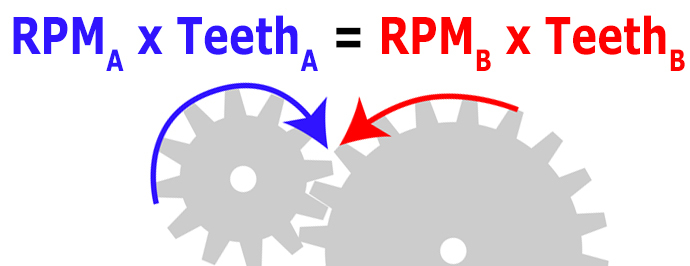
Gear ratio is a measure of the speed relationship between two gears. It represents how many times one gear must rotate for the other gear to complete one full rotation.
Gear ratios are crucial in mechanical engineering as they allow for the modification of torque, speed, and direction of motion in machinery.
Key points about gear ratios:
- A ratio greater than 1:1 indicates speed reduction and torque increase.
- A ratio less than 1:1 indicates speed increase and torque reduction.
- Gear ratios are often expressed as a number followed by a colon and 1 (e.g., 3:1) or as a decimal (e.g., 3.0).
Gear ratios play a vital role in various applications, from simple machines to complex automotive transmissions, allowing engineers to optimize power delivery and efficiency in mechanical systems.
How to compute gear ratio?
Computing gear ratio involves following these steps:
- Identify the driving and driven gears: The driving gear is the one that receives power, while the driven gear is the one that transmits that power.
- Choose a method: Decide whether you’ll use teeth count, gear diameter, or pitch diameter to calculate the ratio.
- Measure or count: Depending on your chosen method, either count the teeth or measure the diameters of both gears.
- Apply the formula: Use the appropriate formula from the ones mentioned earlier.
- Simplify the ratio: If necessary, reduce the fraction to its simplest form.
Example: Let’s say we have a driving gear with a diameter of 2 inches and a driven gear with a diameter of 6 inches.
Using the gear diameter formula:
Gear Ratio = 6 inches / 2 inches = 3:1
How to combine gear ratios?
When dealing with multiple gear pairs in a system, you need to combine their ratios to get the overall gear ratio. To do this:
- Calculate the individual gear ratios for each pair.
- Multiply these ratios together.
Example: In a gearbox with three gear pairs with ratios 2:1, 3:1, and 4:1, the combined ratio would be:
Combined Ratio = 2 × 3 × 4 = 24:1
How to find gear ratio with RPM?
To find the gear ratio using RPM (Revolutions Per Minute), you can use this formula:
Gear Ratio = RPM of Driving Gear / RPM of Driven Gear
Example: If the driving gear rotates at 3000 RPM and the driven gear rotates at 1000 RPM, the gear ratio would be:
Gear Ratio = 3000 / 1000 = 3:1
- Amps To Horsepower Conversion Calculator – Convert Amp to HP
- Horizontal Projectile Motion Calculator
- Polar Moment of Inertia Calculator
- Power to Weight Ratio Calculator – Convert Power to Weight Ratio
- FPS to GPM Calculator – Feet Per Second to GPM Flow Rate Conversion
- Microfarad to Farad Calculator – Convert μF to F
- Convert Kilogram Force Centimeters to Newton Meters – kgf cm to Nm Conversion
- Pounds To Slugs Calculator – Simple lbs to Slug Conversion
- Water Flow Through Pipe Calculator
- Weir Flow Calculator – Calculate Liquid Flow Rates
- Dew Point Calculator – Calculate Dew Point Easily
- RPM to Torque Calculator – Calculating Engine Torque from RPM